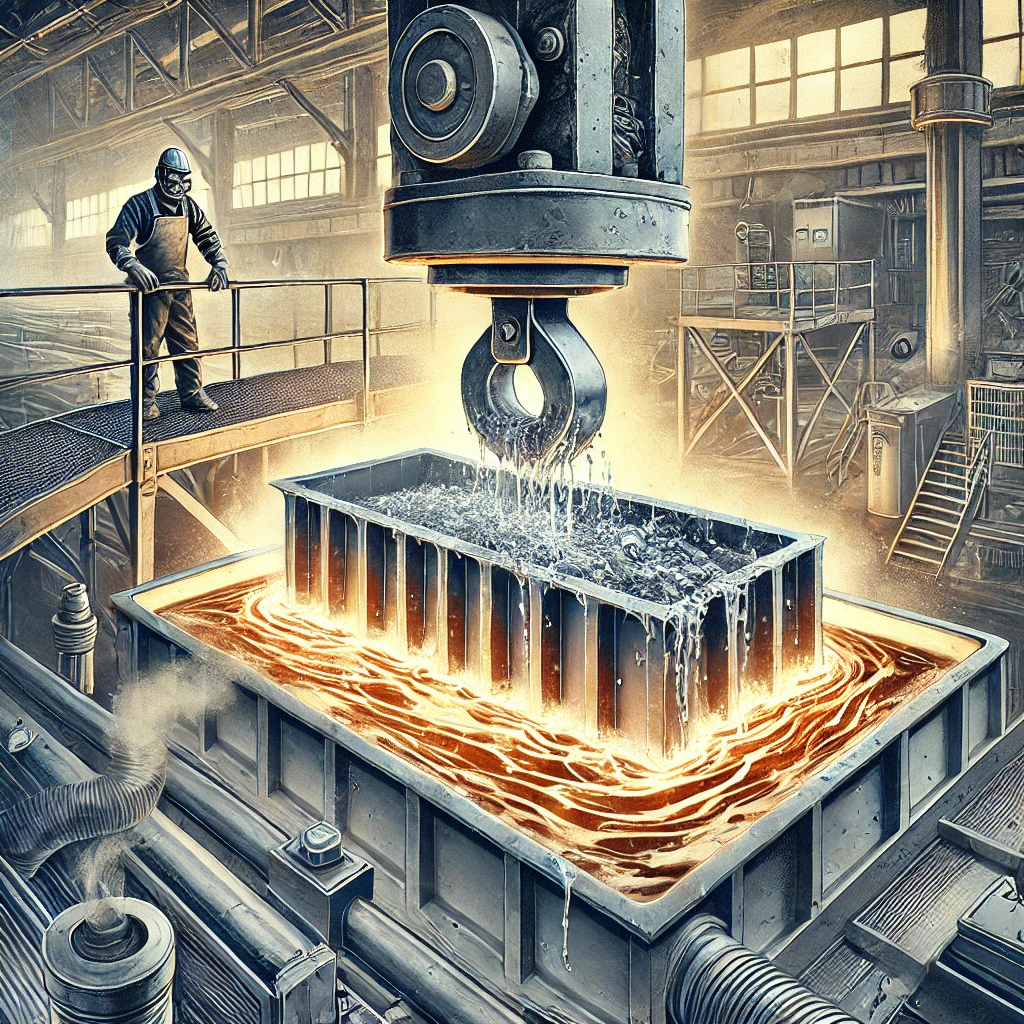
Galvanized coating is a process where a protective layer of zinc is applied to metal surfaces to prevent corrosion, particularly rust. This method is widely used to extend the life of metal products, especially steel and iron, by creating a barrier that shields against moisture and other environmental factors.
How is Galvanized Coating Applied?
There are several methods for applying galvanized coatings:
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: The most common method, where metal is dipped into molten zinc to form a durable, even coating.
- Electrogalvanizing: Involves applying a thin zinc layer using an electric current.
- Galvanizing Spray (Cold Galvanizing): Zinc-rich paint sprayed onto the surface for temporary or less intensive protection.
Each method has its own advantages, depending on the application needs and environmental exposure.
Benefits of Galvanized Coating
- Corrosion Resistance: Provides strong protection against rust, especially in humid or marine environments.
- Durability: Offers a long-lasting solution, often protecting metals for 50 years or more.
- Cost-Effective: Lower maintenance and repair costs due to its longevity.
- Sustainability: Zinc is recyclable, making it an eco-friendly option for metal protection.
- Easy Inspection: Visual checks can quickly determine the integrity of the coating.
Common Applications of Galvanized Coating
- Construction Materials: Steel beams, pipes, and frames for buildings and bridges.
- Automotive Industry: Car bodies and parts that require corrosion resistance.
- Agricultural Equipment: Tools and structures that are exposed to moisture and soil.
- Outdoor Furniture: Benches, fences, and playground equipment.
- Electrical Infrastructure: Power poles, transformers, and transmission towers.
Galvanized coating is a reliable and cost-effective method for extending the lifespan of metal products. Its ability to resist corrosion and provide long-lasting protection makes it indispensable in industries ranging from construction to agriculture.